OSI Layer Model
OSI Layer Model
1. Physical Layer
Transmit raw bit stream
over the physical medium.
2. Data Link Layer
Defines the format of
data on the network.
3. Network Layer
Decides which physical
path the data will take
4. Transport Layer
Transmit data using
transmission protocols including TCP
5. Session Layer
To maintain the
connections and responsible for controlling ports and session
6. Presentation Layer
To ensure that the data
is in a usable format and is where the data is being encrypted occurs.
7. Application Layer
The interaction layer of
the human-computer, where the application layer can access network services
how the data travels from the lecturer’s computer to reach the OnlineLearning System server which is in the Cobham College IT Center
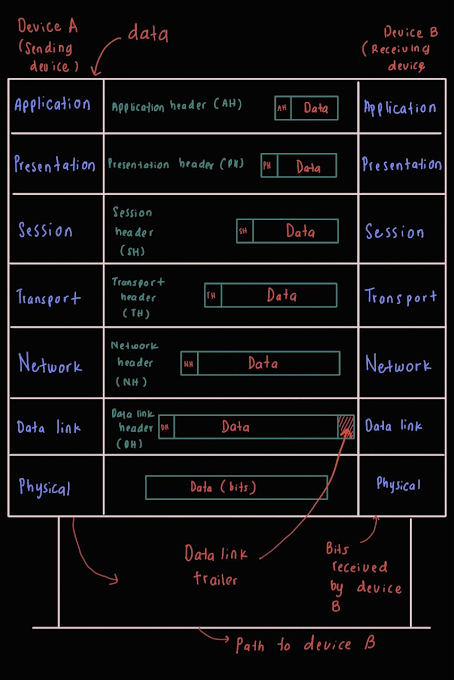
In the OSI (Open
Systems Interconnection) model, data travels through a series of layers, each
of which is responsible for a specific aspect of transmitting the data. Here's
how the data might travel from a lecturer's computer to an online learning
system server using the OSI model:
1. At the Physical
layer, the data is transmitted over a physical medium, such as a network cable
or wireless connection.
2. At the Data Link
layer, the data is divided into smaller units called frames, which are
transmitted over the physical connection.
3. At the Network
layer, the frames are routed to their destination using logical addressing
(e.g., IP addresses).
4. At the Transport
layer, the data is divided into smaller units called segments, which are
transmitted over the network connection. The Transport layer is responsible for
ensuring that the segments are delivered reliably to the destination.
5. At the Session
layer, the data is organized into a series of dialogues or "sessions"
between the two devices.
6. At the
Presentation layer, the data is converted into a standard format that can be
understood by both the sender and receiver.
7. At the
Application layer, the data is delivered to the online learning system server
and is processed according to the specific application being used (e.g., a web
browser).
The possible network components involve throughout the communications.
Network Devices: Network devices, also
known as networking hardware, are physical devices that allow hardware on a
computer network to communicate and interact with one another. For example,
Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Routers, Gateaway, Router, and NIC, etc.
For this scenario, there are a few
possible network components throughout the communications:
1. Physical Layer:
Hub – A hub connects multiple wires
together from different branches so that they function as a single network.
Data has to pass through the hub before it can be sent to other devices which
in this case is from the home network to the IT centre.
Cable – A cable is simply a device to
connect two devices for the purpose of establishing a connection. In this case,
an ethernet cable is used to form a connection between a device to the hub.
Repeater – A hub is basically a
multi-port repeater which functions to regenerate signal over the same network
to extend the length to which a signal can be transmitted. This allows the
connection between home network with the online learning system to not be
corrupted.
2. Data Link Layer:
Switch – It works similarly as the hub
but there’s a major difference in where the switch can perform error checking
before forwarding data, which makes it very efficient as it does not forward
packets that have errors and forward good packets selectively to the correct
port only.
Bridge - The basic purpose of a bridge
is to forward the frames to their destination.
3. Network Layer:
Router - A router is a device like a
switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses. It functions to
receive the packets from the data link layer and forward them to their
destination.
4. Session Layer:
Gateway – It is a passage to connect
two networks that may work upon different networking models. They work as
messenger agents that take data from one system, interpret it, and transfer it
to another system which is the presentation layer.
5. Application Layer:
Encryption device: It is capable of
encrypting the data which is to be sent over the network. In this case, HTTPS
commands can be read and granted permission to the user to access the website.



Comments
Post a Comment